
When discussing PSUs(Power Supply Unit) many of us might not give them as much importance as we do to core components like CPU,Motherboard, and storage drives. However, the PSU is the only component that powers all the core components of your PC.

It is crucial to choose the right power supply for your PC.Paying too little attention to this hardware could decrease performance or even damage other components.
Basically, the power supply converts the AC(Alternating Current) from the wall outlet into DC(Direct Current) and provides the power to all the other components that required.It plays a vital role in the ovcrall performance of your systems.
After all,the power supply determines whether your system receiving enough wattage to run properly .That’s why choosing a right PSU is essential.
So,in this blog post, I will cover some major factors that are required to follow and some certifications while choosing a power supply.
What is a Power Supply
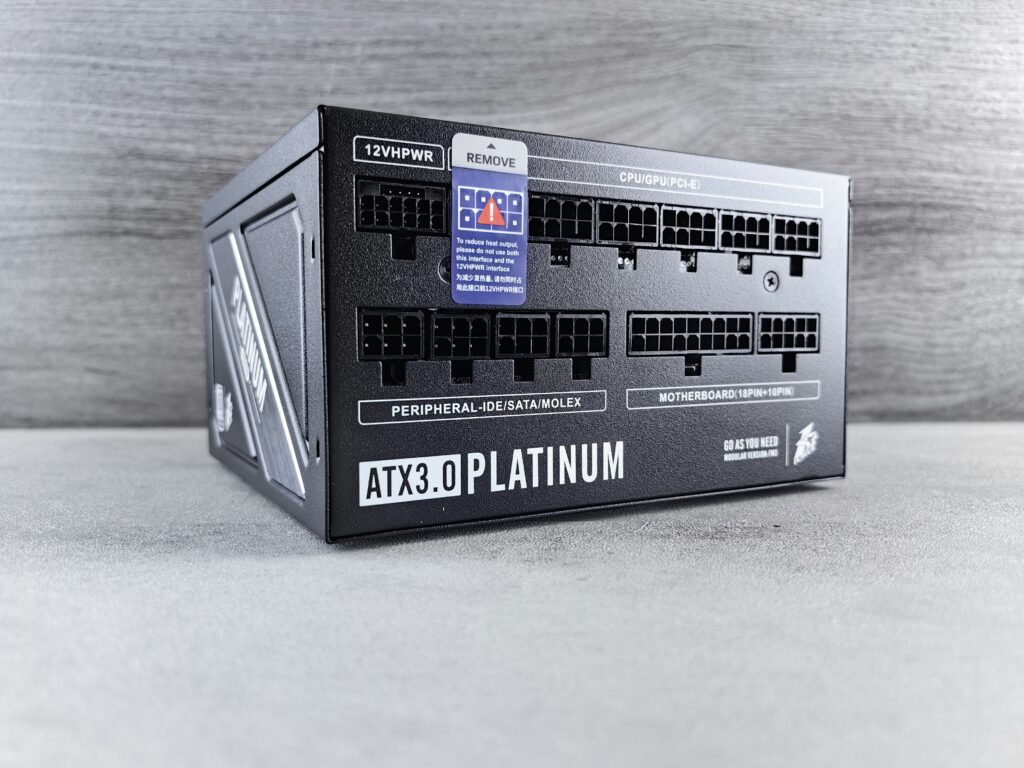

A Power supply is a square metal box with a bunch of wires emerging from one with connectors that fit inside the computer case.
A power supply can come in different shapes and form factors.The most common form is ATX
A Power Supply delivers all the power that your components need to run efficiently.It converts the AC power into DC as a intermediary and provides the power through a 12-volt that your PC can use.The power supply distributes power through various voltage rails,such as 12V,5V, and 3.3V and ensures that all the components are getting enough wattage for optimal performance.
Power Connectors
There is a main power connector in Power Supply which is called the P1 connector.It’s the power source that delivers power to all the components in different voltage rails as needed by major components like CPU,RAM,GPU etc.
In the early days,the P1 connectors usually came with 20 pins, but in modern times they come with 24-pins socket.
Another connector specifically dedicated to supplying power to processors is the P4 connectors.It is a 4-pin ATX12V connector that supplies delivers to the CPU and plugs into the CPU socket on the motherboard.Before this connector existed,some CPUs lacked a stable voltage source and drew power inefficiently.To address the issue, Intel introduced the 4-pin connector.
As technology advanced, the P4 connectors failed to supply adequate voltage to modern CPU’s ,To address this issue, the P8 connector—also known as EPS—was introduced. This 8-pin connector plugs into the motherboard and provides the necessary power for high-performance processors.
Understanding Power Supply Wattages: Choosing the Right PSU for Stable and Efficient PC Performance
Power Supply Voltage Rails and Their Functions
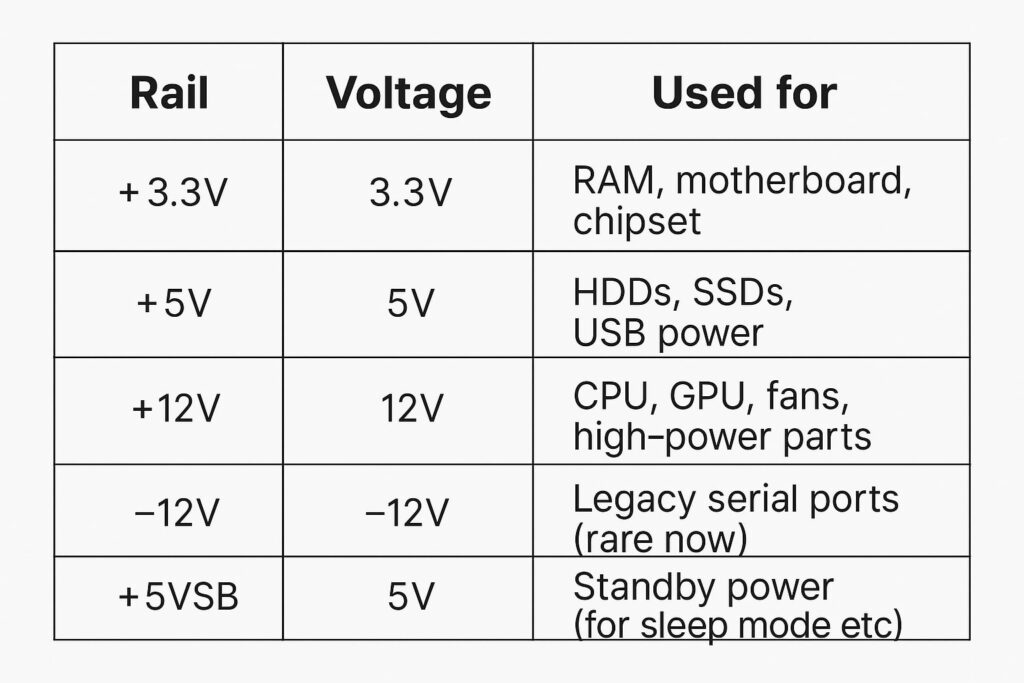
Power supplies also come with different wattages.They depend on the number of components that need power.Starting at 200W, they range up to 2000W for different power supply models.
For example,If you have a system that has minimal components you just need a low-wattage power supply.Conversely, If you have a high-end PC that has a lot of components such as multiple drives,RGB lighting, multiple gaming cards, you will definitely need a high-wattage power supply.
An average PC today need a power supply anywhere between 500W and 600Watts.On the other hand, a high-end enthusiast’s PC may need a power supply around 1000 watts or even more.
If you’re having trouble finding how much wattage your systems needs, you can use any online calculator to help you calculate the correct wattage for your power supply.Here are some websites you can visit to easily find out the wattage with basic input.
Coolermaster.com – Quick and simple to use for beginners.
seasonic.com – Reliable and easy for finding the correct PSU models.
Tip: Always aim to leave some space. For example : If an online calculator suggests 650W, go with 750W .That will help you with future upgrade.
After finding the correct wattage, let’s move on the next section, which covers the categories of power supplies: Non-Modular, Fully Modular and Semi-Modular. The differences between these lie in how the cables are attached to the power supply.
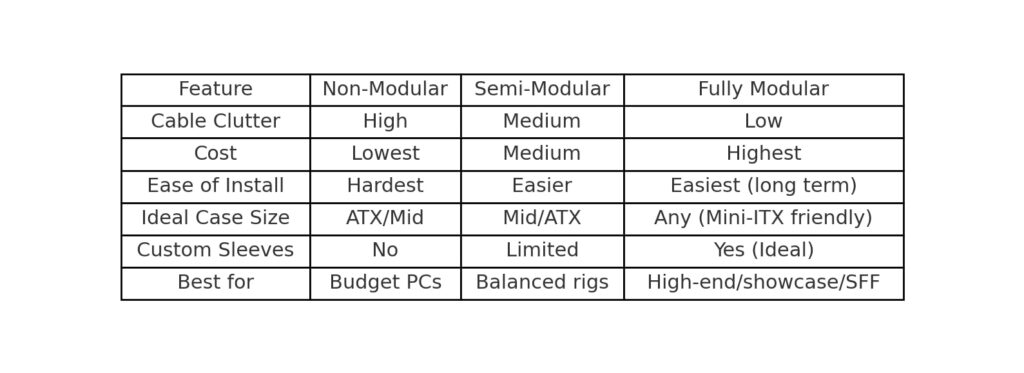
Non-Modular Power Supply: All the connector cables(SATA,CPU,24-Pin etc) are permanently attached to the power supply.There is no option to detach any cables.If any cables are not being used, you can’t remove them. As a result, this leads to poor cable management, which can cause higher temperatures.
This types of PSU are usually cheaper among the options and are good for basic builds where looks doesn’t matter.
Ideal for:Budget Builds.
Office or general uses.
Semi-Modular Power Supply:In semi-modular power supply, some neccessary cables are attached while others are detached.For instance,24-pin and 8-pin CPU(EPS) cables are permanently attached to it.On the other hand,cables like SATA cables,PCle for GPU’s are detachable.This makes the power supply a mix of hybrid and customizable cable management.
Ideal for:Gamers and content creators
PC enthusiasts from mid-range to upper mid-range
Fully-Modular Power Supply:Now comes the Fully-Modular Power Supply.In this power supply, you can manually attach or detach any cables as needed, making it much more convenient compared to other PSUs.If you don’t need unnecessary cables based on your requirements ,you can simply detach them, ensuring better airflow as well as improved cable management.
Ideal for: High-end gamers and professional workstation builds
PC enthusaists
80 Plus Certification for Power Supply:
The 80 Plus cerfication determines the efficiency of a power supply at different loads.PSU’s are rated as 80 Plus Bronze,Silver or Gold. These terms indicate that the PSU will provide a certain level of efficiency at different load percentages(e.g,, 20%,50% or 100% load)